Description
Generic Pulse Waveform is used for experiments that require a repeating square-wave pulsed waveform in which the characteristics of the pulse can be easily modified. Pulse plating is a common application of the Generic Pulse Waveform. Battery, fuel-cell, and sensor developers may also need the Generic Pulse Waveform. The generic pulse can be under either Potentiostatic or Galvanostatic control.
The Generic Pulse Waveform may be used with a solid electrode (e.g., Pt, Au, glassy carbon), a rotating electrode, or a Hanging Mercury Drop Electrode.
The type of electrode chosen determines whether mercury-drop formation signals are generated. The Purge & Stir information determines whether de-aeration (purge) and stir signals are output.
Applied Waveform and data acquisition
The Generic Pulse Waveform allows you to completely define a square wave to apply to a sample. The waveform is shown in the figure below.
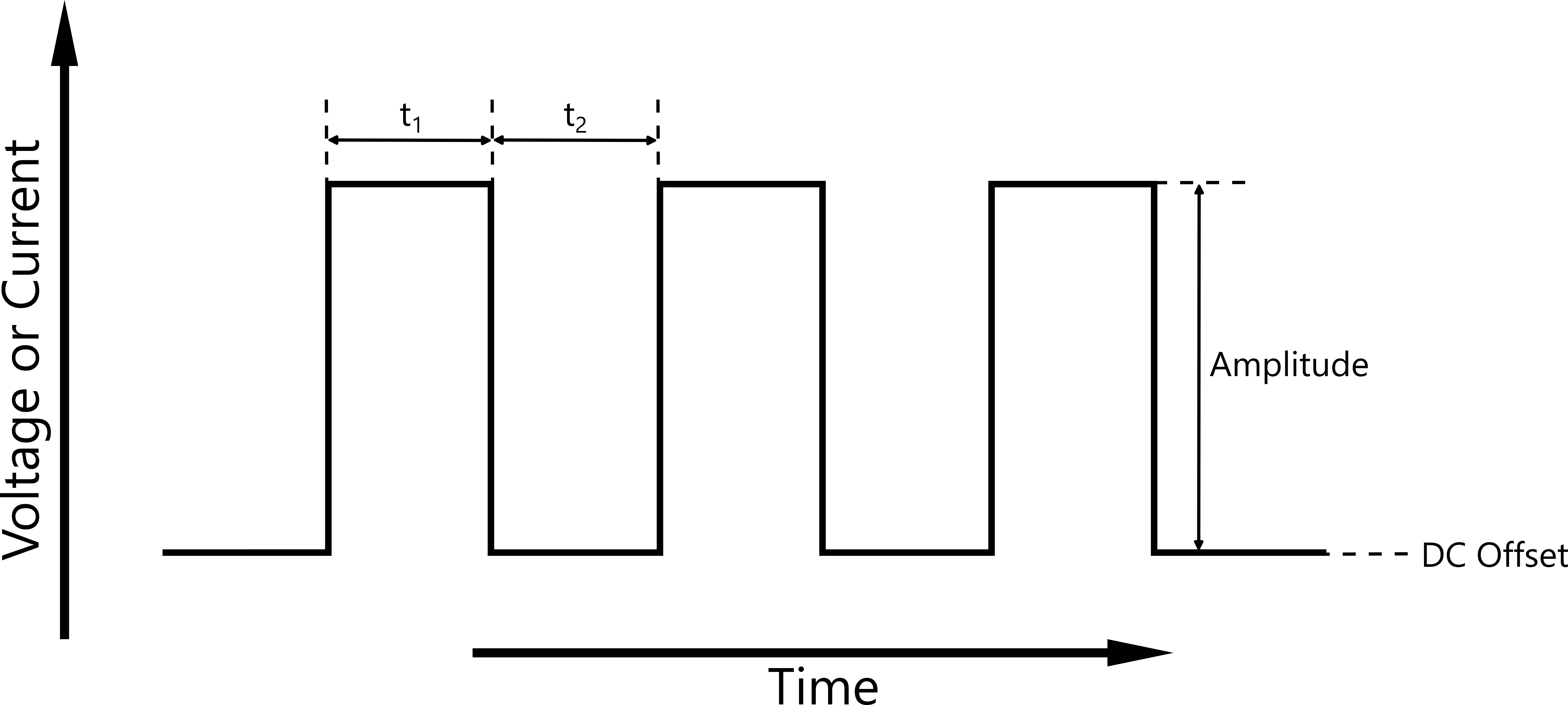
Step signal for Generic Pulse Waveform.
The signal levels are defined by the DC Offset value combined with the Amplitude of the square wave. The minimum value for t1 and t2 is 1 ms. The square wave may be asymmetrical, i.e., t1 and t2 may have different values.
There are three modes of current or potential measurement:
•Measure the current or potential every 1 ms or longer.
•Measure the last point prior to the upcoming pulse.
•Enable Noise Rejection to allow data-point averaging and achieve the highest signal-to-noise ratio.